
An ultrasound performed in early pregnancy, typically between 7 and 12 weeks, to confirm pregnancy, determine gestational age (how far along the pregnancy is), and estimate the due date.

Refers to a combination of prenatal screening tests, specifically First Trimester Screening (FTS), Enhanced First Trimester Screening (eFTS), and Nuchal Translucency (NT) with Nasal Bone (NB) scan.

NIPT (Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing), is a prenatal screening test that analyzes fetal DNA found in the mother's blood to assess the risk of certain chromosomal abnormalities in the developing fetus.
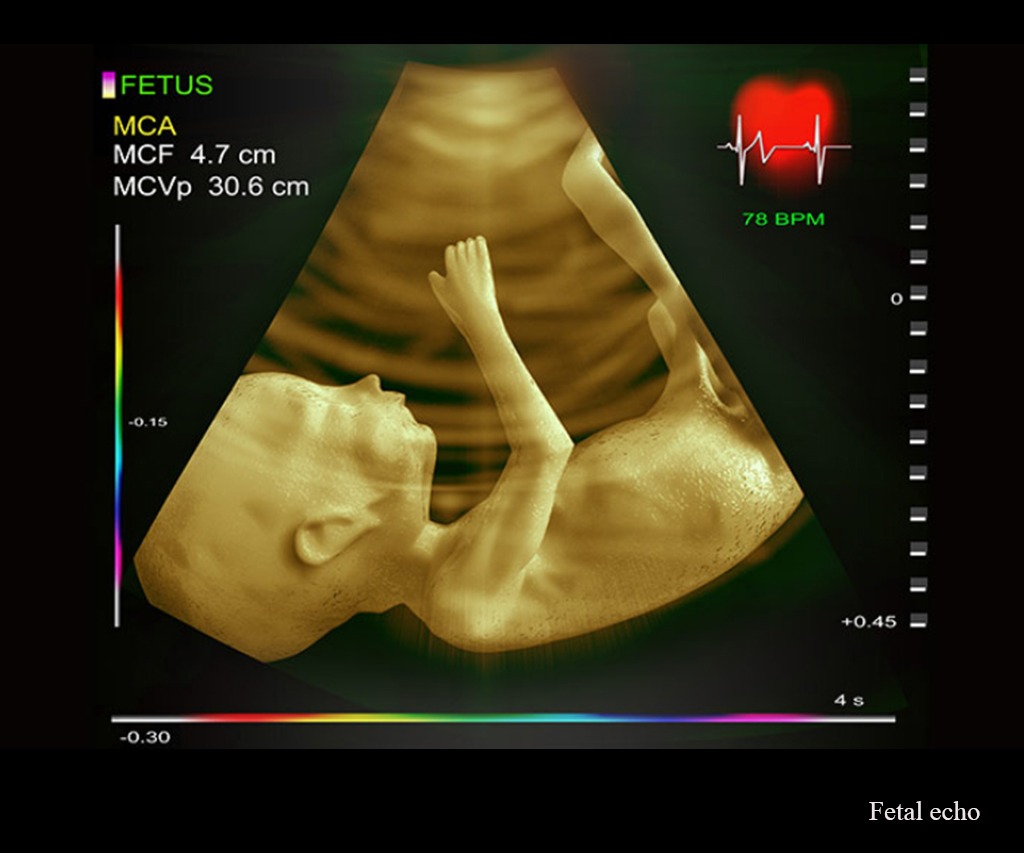
A fetal echo, or fetal echocardiogram, is a specialized ultrasound that examines the developing baby's heart in the womb. It's a detailed assessment that can identify congenital heart defects (CHDs) before birth.

The process of providing individuals and families with information about genetic conditions, helping them understand the medical, psychological, and familial implications of these conditions.
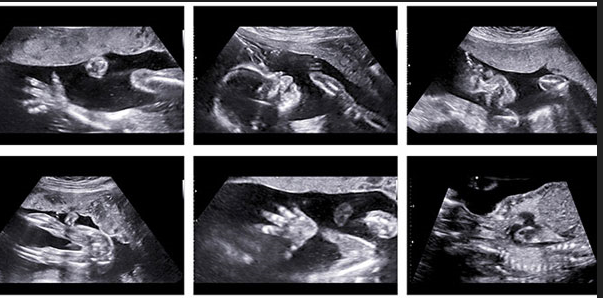
Both Early Anomaly Scan and Anomaly Scan are ultrasound scans during pregnancy that help detect abnormalities in the developing fetus.
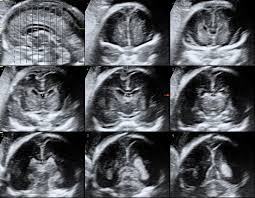
Fetal neurosonogram (also called fetal neurosonography) is a detailed ultrasound scan of a baby’s brain and spinal cord performed during pregnancy. It provides in-depth imaging of the fetal central nervous system (CNS) — primarily the brain and upper spine — to detect abnormalities or monitor development.
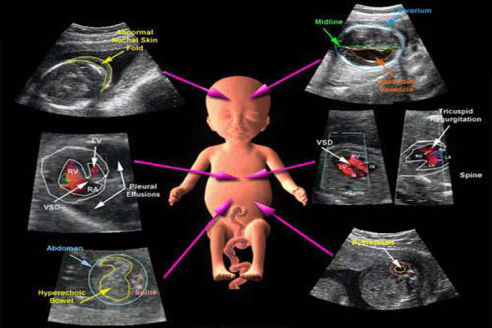
Growth and Doppler scans are advanced prenatal ultrasound tests that are typically done in the third trimester of pregnancy (after 28 weeks), especially when doctors need to closely monitor the baby’s development or if there are any concerns.
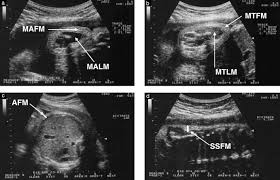
IUGR (Intrauterine Growth Restriction) pregnancy scans are specialized ultrasound assessments used to monitor the growth and health of a fetus that is not growing at the expected rate during pregnancy.
Hemophilia and Thalassemia screening are medical tests done to identify whether a person has, or is a carrier of, two specific inherited blood disorders: Hemophilia and Thalassemia.
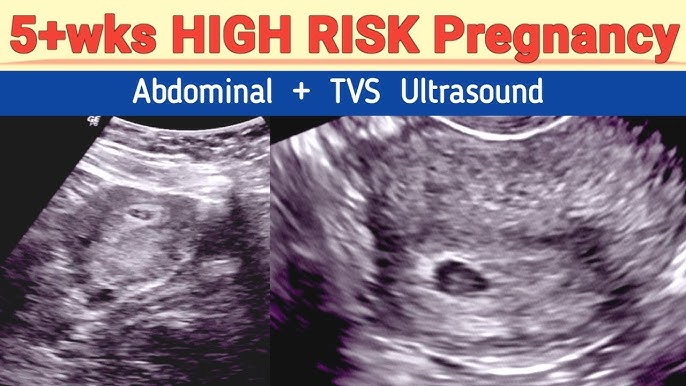
High-risk pregnancy scanning refers to a series of specialized ultrasound and diagnostic tests performed during pregnancy when the mother or baby has a higher-than-normal risk of complications.
Down syndrome causes intellectual disability, developmental delays, and certain physical features. It varies in severity and can also lead to other health issues such as heart defects.
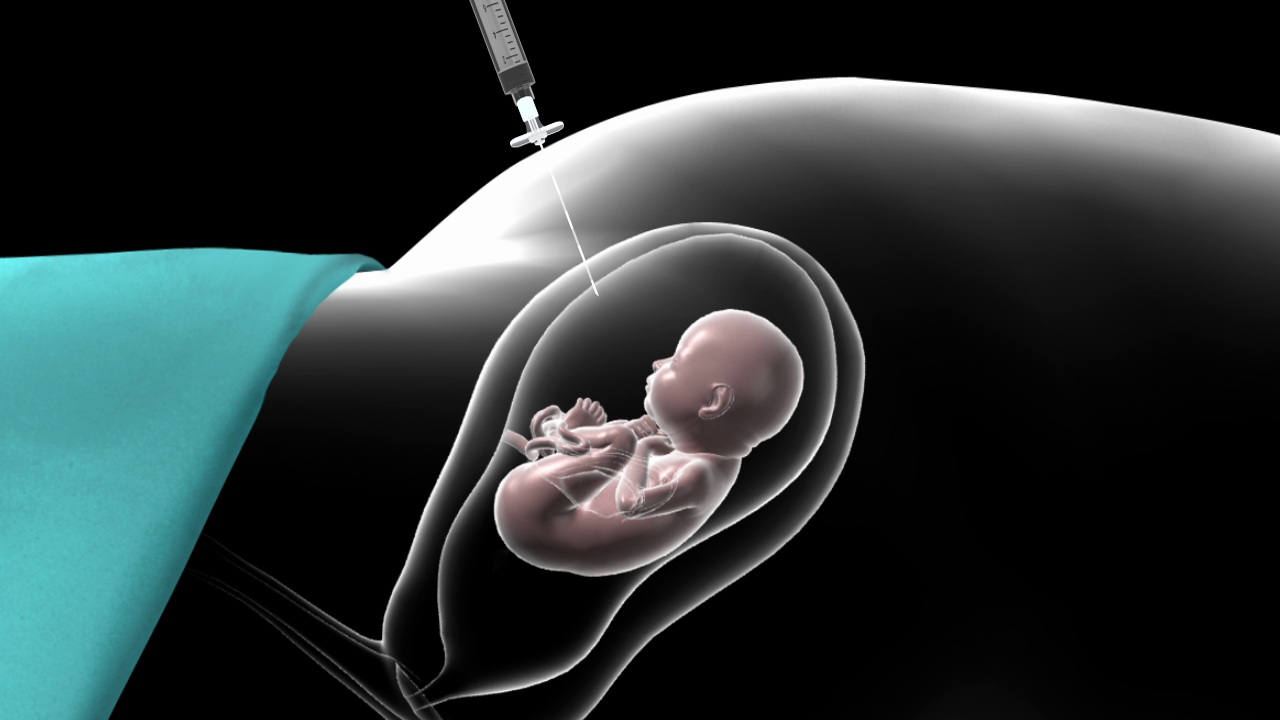
Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic procedure used to assess the health and development of a fetus during pregnancy. It involves removing a small amount of amniotic fluid
Twin pregnancies require more frequent and specialized ultrasound monitoring compared to single pregnancies. Scans are crucial for determining chorionicity (whether twins share a placenta)